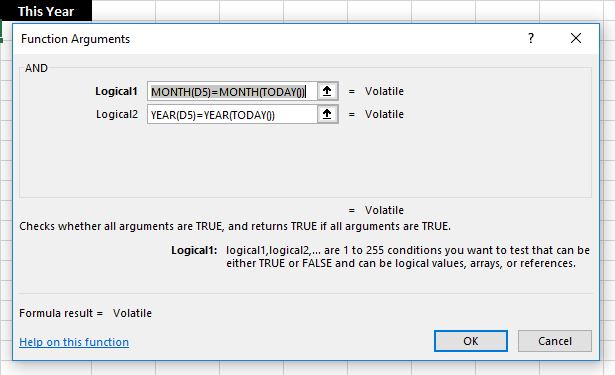
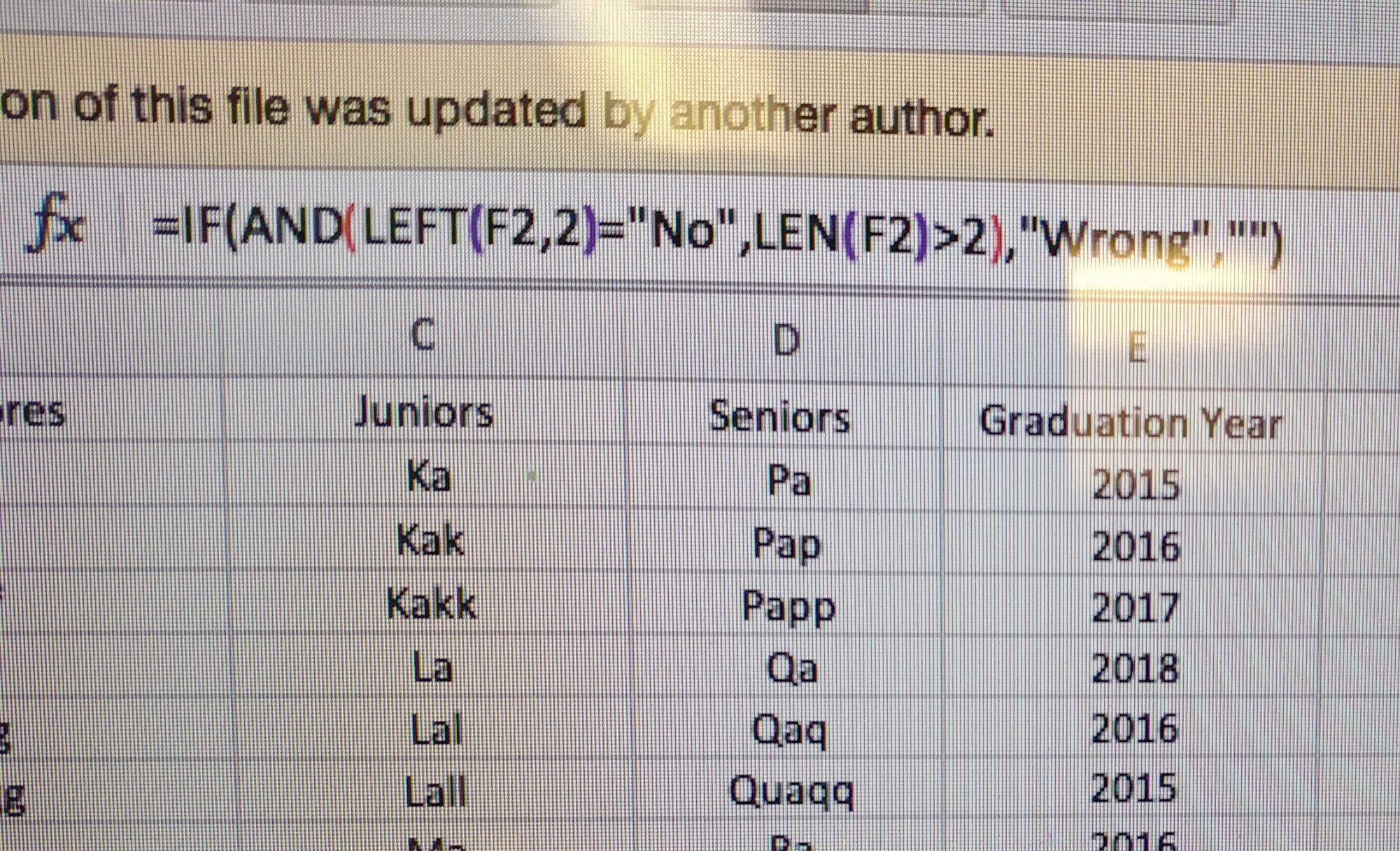
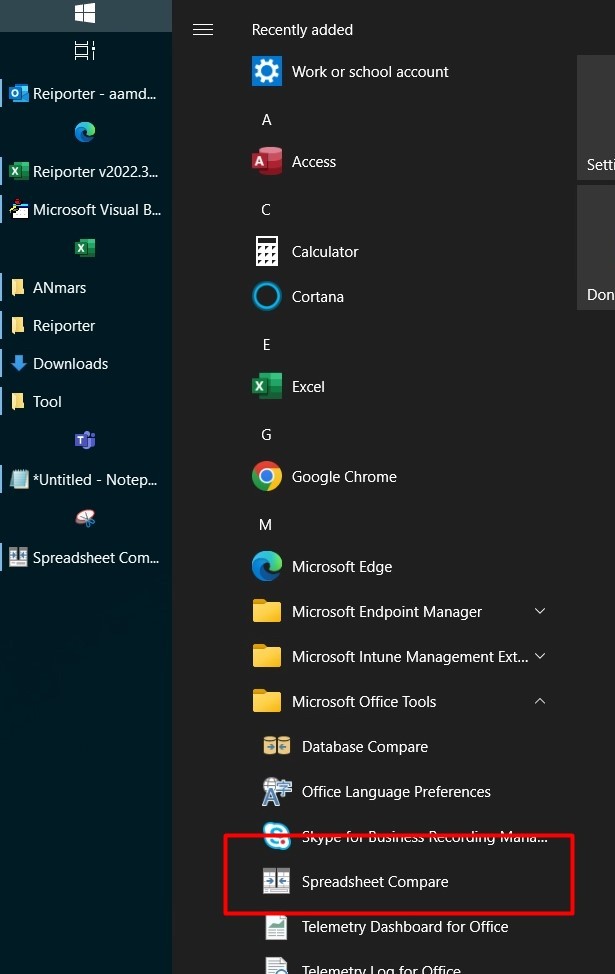
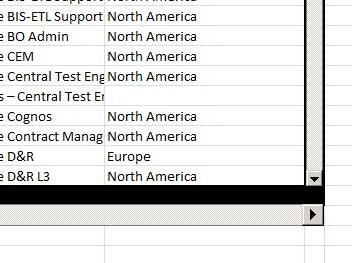
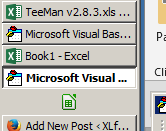
Excel 2010 was great because you can easily open another Excel session while your current session is working.
This allowed us to run multiple tools at the same time, since those two sessions are separated and do not touch.
However, starting Excel 2013, the interface changed, making it harder to run new session or open Excel while we have another Excel session running some long process.
that is when we start to look around and found a solution
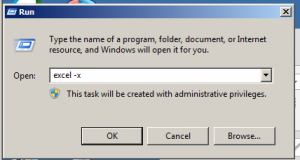
you can FORCE Excel to open another separated session by running command line in run
Excel -X
This way, you can have two separated Excel sessions that do not affect each other, and we can now run several instances of our long macros.